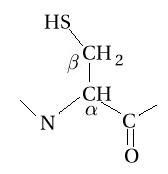
The formula of an amino acid comprises, bound to a carbon (alpha carbon):
- a carboxyl group -COOH
- an amine group -NH2
- an atom of hydrogen -H
- a variable radical -R, that is the functional group (in red in the table) of the amino acid.
Chemically speaking, an amino acid is a carboxylic acid which has an amine group attached to it. The general linear formula of an amino acid is R-CH(NH2)-COOH.
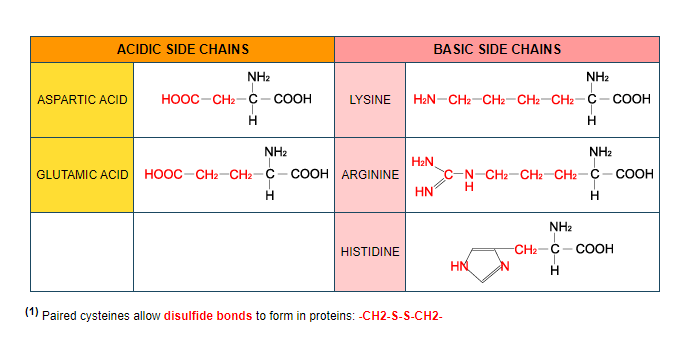
The 20 common amino acids are grouped in classes according to their side chains:
Click here for IMGT classes of the 20 common amino acids ‘Physicochemical’ properties.
Structural formula
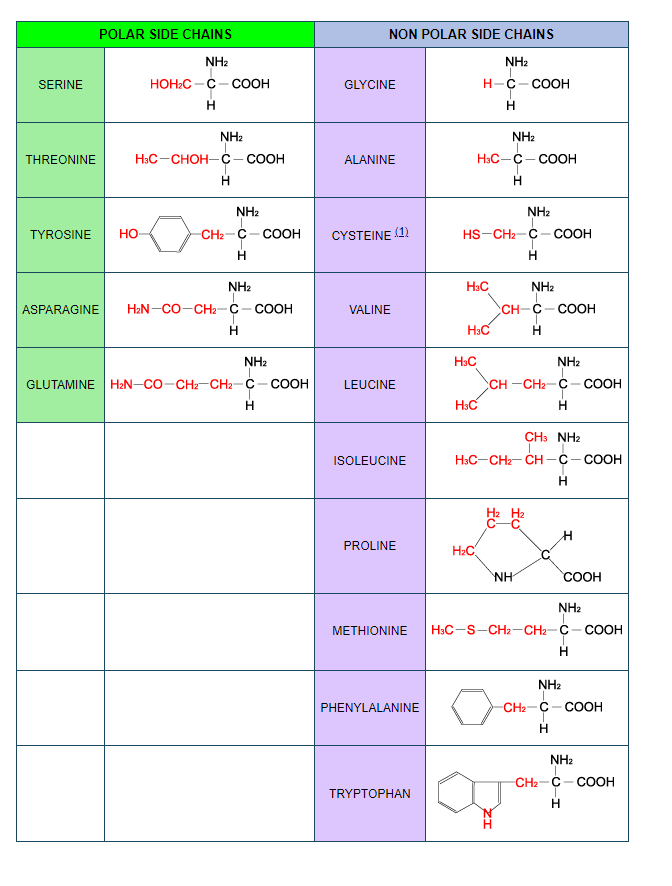
Charged side chains are POLAR.
| Amino acid | Abbreviations | Molecular formula | Linear formula | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | Ala | A | C3H7NO2 | CH3-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Arginine | Arg | R | C6H14N4O2 | HN=C(NH2)-NH-(CH2)3-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Asparagine | Asn | N | C4H8N2O3 | H2N-CO-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D | C4H7NO4 | HOOC-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Cysteine | Cys | C | C3H7NO2S | HS-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q | C5H10N2O3 | H2N-CO-(CH2)2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E | C5H9NO4 | HOOC-(CH2)2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Glycine | Gly | G | C2H5NO2 | NH2-CH2-COOH |
| Histidine | His | H | C6H9N3O2 | NH-CH=N-CH=C-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I | C6H13NO2 | CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Leucine | Leu | L | C6H13NO2 | (CH3)2-CH-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Lysine | Lys | K | C6H14N2O2 | H2N-(CH2)4-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Methionine | Met | M | C5H11NO2S | CH3-S-(CH2)2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F | C9H11NO2 | Ph-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Proline | Pro | P | C5H9NO2 | NH-(CH2)3-CH-COOH |
| Serine | Ser | S | C3H7NO3 | HO-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Threonine | Thr | T | C4H9NO3 | CH3-CH(OH)-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W | C11H12N2O2 | Ph-NH-CH=C-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y | C9H11NO3 | HO-Ph-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH |
| Valine | Val | V | C5H11NO2 | (CH3)2-CH-CH(NH2)-COOH |
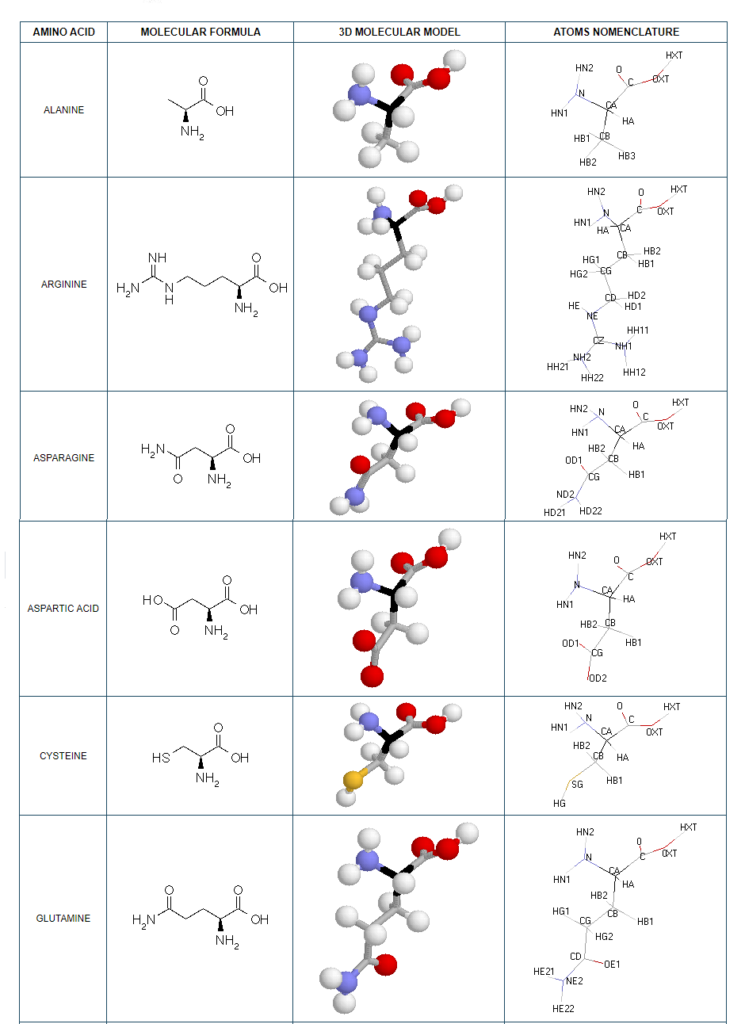
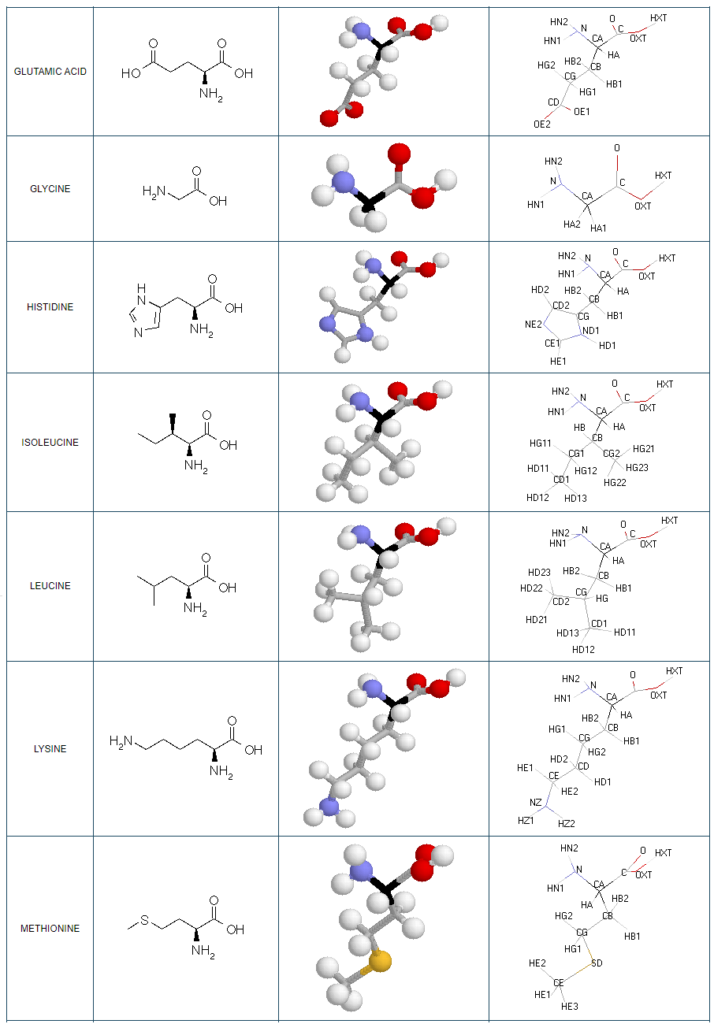
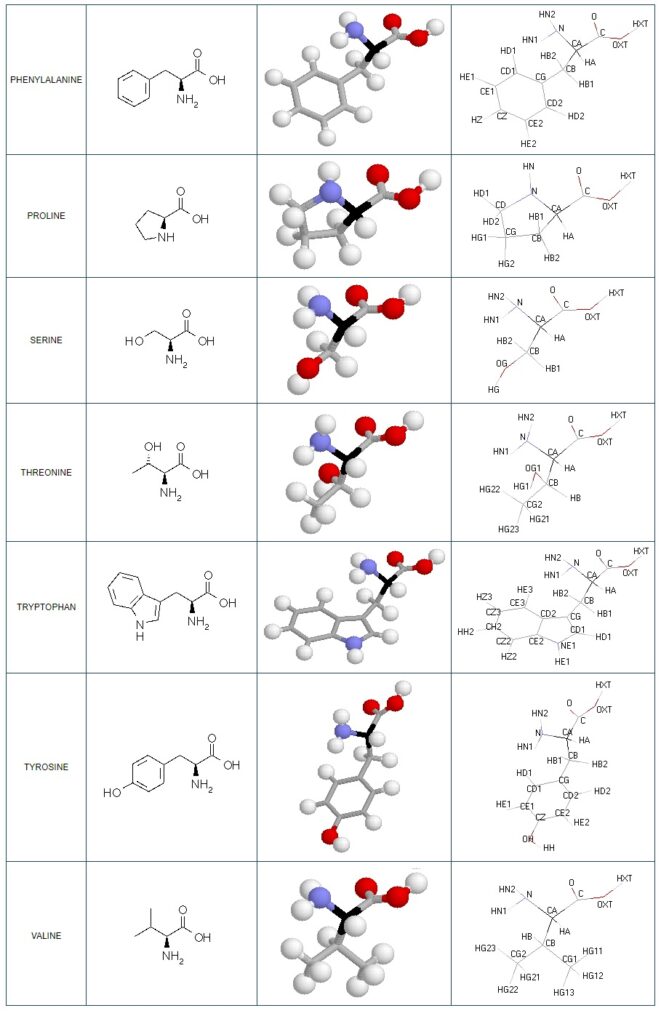
Structural details of the side chains: formula, 3D model and atoms nomenclature
The general formula of an amino acid is composed by a carbon alpha atom, a carboxyl group, a side chain group and an amino group.
- Molecular formula: structural formula with the carbon alpha atom and the radical of each amino acid.
- 3D molecular model: a ball and stick model of the amino acids is shown. Oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur atoms are represented by colored spheres (Oxygen: red, Hydrogen: white, Nitrogen: blue, Sulfur: yellow). The carbon alpha atom is represented by black sticks and other carbons by grey sticks.
- Atoms nomenclature:
- CA : Carbon alpha
- HB : Hydrogen of carbon beta
- HN : Hydrogen of nitrogen
- OXT : Oxygen of hydroxyl
- HXT : Hydrogen of hydroxyl
- Representation of an amino acid example (cystein) engaged in a peptide chain and showing the carbone alpha and the carbone beta.