What is Solid Phase Extraction (SPE)?
Solid phase extraction (SPE) is a common sample pre-treatment technique. It’s developed from solid liquid extraction and chromatography methods and is often used for sample fractionation, purification, enrichment and concentration.
Similar to Liquid Chromatography (LC), in SPE process, interfering components get seperated from analytes due to the difference of affinity and adsorption.
SPE is one of the most common sample pre-treatment techniques before HPLC, LC, GC MS analysis for being easy to operate, able to simplify analyst and increase sensitivity. The major advantages of using SPE include:
- Make sample simpler and cleaner.
Samples often have complex composition. The interferents may reduce sensitivity and further reduce the lifespan of columns and instruments. SPE treatment can acquire clean extraction of analyst and more accurate results. - Concentration and trace enrichment.
SPE benefits when researchers need to hit low detection, for example, ppb (10-9) or ppt (10-12), because SPE process can help sample enrichment and purification very easily. - Compound fractionation.
SPE can separate multiple compounds from samples according to specific characteristic like polar or non-polar.
SPE、LLE、SLE Comparison
Statistically, sample preparation and pre-treatment take 80% of time and costs in modern scientific analysis. Simpler and faster pre-treatment methodology can create obvious benefits for all scientists.
Other than SPE, there’re several other commonly used sample pre-treatment methods, like Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE), Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) and Protein Precipitation (PPT).
| Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) | Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) | Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) | |
| Method development | Required | Required | Required |
| Pollution factors | Less solvent and plastic wastes | A lot solvent wastes | Some solvent and plastic wastes |
| Operational safety | Safe (exposure to solvent) | No safe (exposure to solvent, potential to explosion) | Safe (exposure to solvent) |
| Main costs | Extraction Column | Solvent, powdered solvent | Extraction Column |
| Sample requirement | Less | More | Middle |
| Emulsion | None | Yes | None |
| Sensitivity | High | Low | Middle |
| Heating concentration | Not required | Required | Not required |
| Automation | Possible | Not possible | Possible |
| Speed | Middle | Slow | Fast |
| High throughput | High | Middle | High |
| Limitation | None | Not suitable for very polar analytes | None |
Steps of Solid Phase Extraction Process
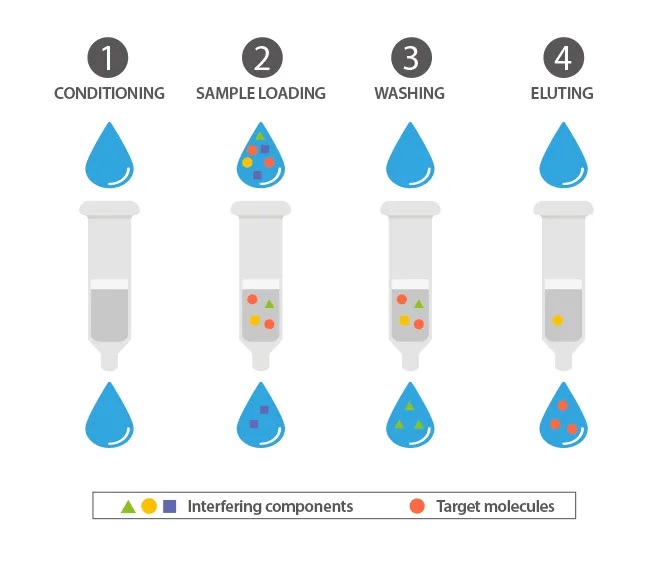
There are 4 major steps of solid phase extraction process:
- Conditioning: Priming the cartridge for it to accept the analyte of interest.
- Sample loading: Load the sample at suitable flow and let target analytes get adsorbed/collected by the adsorbent.
- Washing: Rinse with solvent or 100% H2O to remove un-retained interferents. More rinses can then be done with increasing percentages (ex.: 5%, 10%, 20%, 100%) to remove compounds in terms of decreasing polarity.
- Elution: Release analytes from adsorbent.
Solid Phase Extraction Applications
- Pharmaceutical industry, such as components extraction and research of metabolite.
- Environmental Analysis, such as extraction of metals in water.
- Food testing, such as pesticide and veterinary drug residues.
- Switch sample matrices to be more compatible with the target chromatographic method.
- Concentrate analytes (trace enrichment) for increased sensitivity.
- Remove interferences that cause high background, misleading peaks, and/or poor sensitivity during chromatographic analysis.
- Protect the analytical column from contaminants. Automate the extraction process.
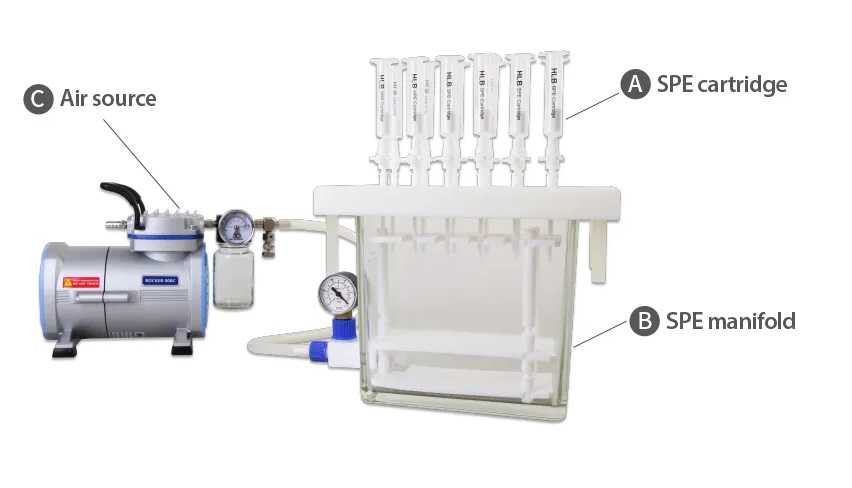


The most common SPE type is adsorption, which is to install SPE cartridge containing adsorbents onto a filter device. To accelerate the exchange process, air pressure devices can be involved.
A. SPE cartridge / SPE column
It may various types include column, membrane, 94-well microplate or pipette tips filled with adsorbents.
B. SPE manifold
A device to place cartridges or membranes.
| SPE Manifold (Column type) | SPE Manifold (Membrane type) |
C. Other device
Most common device used in SPE process is air compressor or vacuum pump that help accelerate liquid flow. However, high speed of flow may cause lower reaction, thus a pump/compressor with regulator is suggested. Furthermore, since SPE process often involve solvents like methanol or acetonitrile. To ensure device lifespan and safety during operation, devices with chemical resistance are highly recommended.
References:
- WatersTM Beginner’s Guide to SPE
- Mass Spectrometry for the Clinical Laboratory, 2017, Pages 37-62
- Comprehensive Sampling and Sample Preparation, 2012
- Solid Phase Extraction Guide, Thermo Fisher